Nature of Damage:
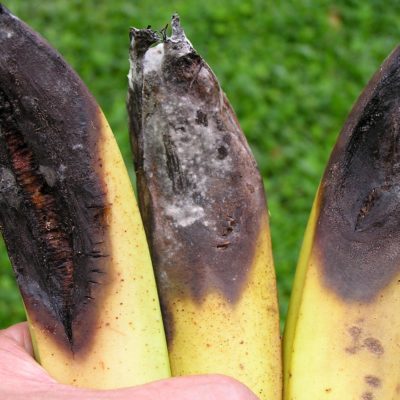
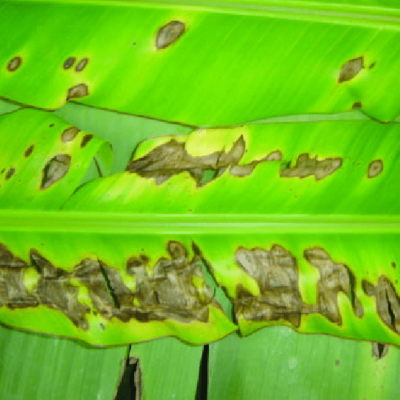
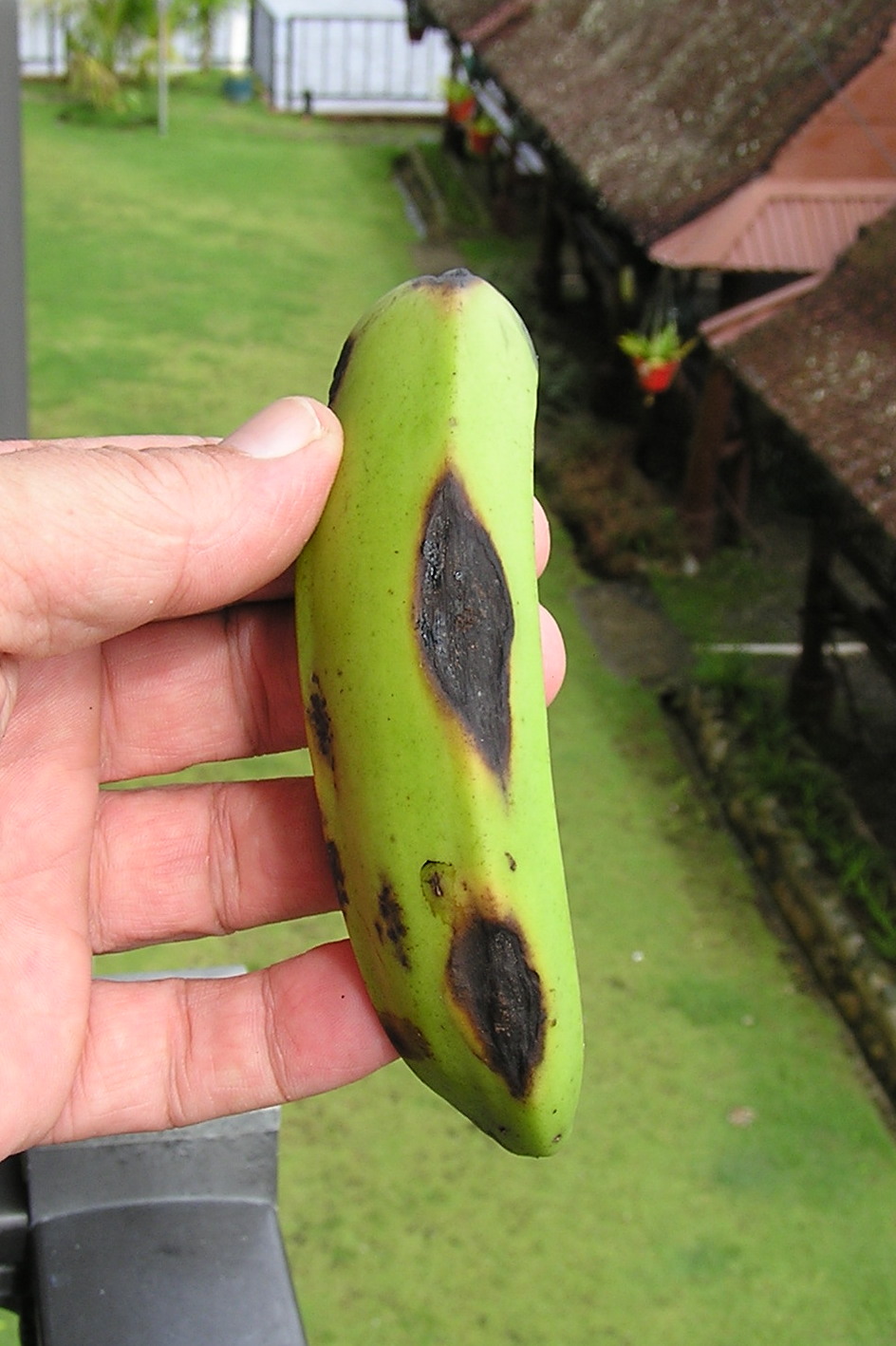
- The fungus attacks the young banana fruits usually at the distal end.
- At the initial stage, small, circular, black spots develop on the affected fruits. Then these spots enlarge in size, turn to brown color.
- The skin of the fruit turns black and shrivels and becomes covered with characteristic pink acervuli. Finally the whole finger is affected. Later the disease spreads and affects the whole bunch.
- The disease results in premature ripening and shrivelling of the fruits which are covered with pink spore masses.
- Occurrence if black lesions on the pedicel causes withering of the pedicel and dropping of the fingers from the hands.
- Become black and rotten.
Cultural Control:
- Burn the infected materials
- Proper field sanitation
- Practice crop rotation with paddy or sugarcane
- Keep the field free of weeds and provide good drainage
- Fruit should be free from infection and as possible before it is transported, stored and ripened
- Banana bunches should be harvested at correct stage of maturity.
- Proper fertilization prevents the infection
Chemical Control:
- Protective spraying when the fruit is still young with Bordeaux mixture 1%
- Pre-harvest spray with Prochloroz 0.2% or Carbendazim 0.1% or Chlorothalonil 0.2% four times at fortnightly intervals is highly effective
- Post-harvest dipping of fruits in mycostatin 440 ppm or Aureofunginsol 100 ppm or Carbendazim 400 ppm or Benomyl 1000 ppm.
Mechanical control:
- The distal bud should be removed when all the hands opened to prevent infection
- After harvest, the bunches should be transported to the store house without causing any bruises to them. The transported bunches should be stored carefully at 7 to 10°C
- Avoid contamination in collecting places, during transport and in ripening rooms