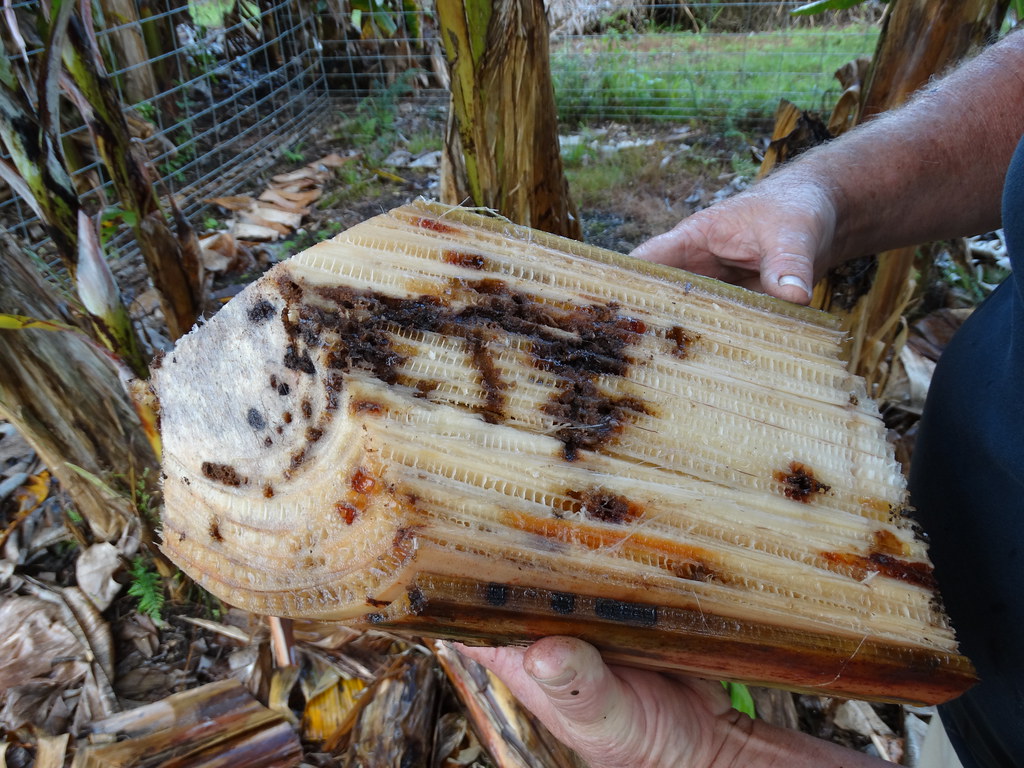
The grub of corm weevil attacks the plant by feeding on the corm portion and thereby making bore holes and tunnels in the corm. Infestation at the early stage reduces the plant vigour.
Nature of Damage:
- Newly planted banana fields are easily susceptible to infestation
- Infestation begins at the base of the outer most leaf-sheath and in injured tissues at the lower part of the pseudo stem.
- Initially the young grubs make several longitudinal tunnels in the surface tissue until they are able to penetrate to adjacent inner leaf-sheaths
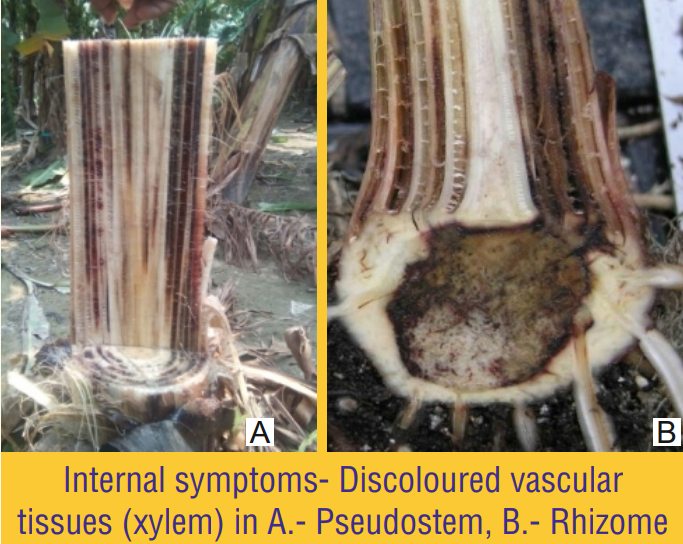
- Then they bore into the pseudo stem base and rhizome/corm, but also into the base of suckers and into roots.
- Larval tunnels may run for the entire length of fallen pseudo stems.
- Infested plant shows yellowing and withering of leaves, slowed plant growth, root destruction, reduced fruit production
- Young infested suckers often wither and fail to develop.
- Plants are easily blown down by mild to strong winds.
- An economic threshold of 3 weevils per cut banana corm or pseudo stem placed in the field overnight will trigger control action
Identification of Pests:
Egg: Elongate-oval, about 2 to 3 mm long and white in colour. Eggs are laid singly in small cavities that are chewed out by the female in the base of the pseudostem just above ground level, in the upper part of the corm, in roots near the soil surface and at the end of cut stems (stumps). Egg period is 4 to 36 days depending on temperature conditions.
Grub: Creamy white legless grubs, stout and distinctly curved and swollen in the middle of the body. The head is reddish-brown with strong mouthparts. Fully-grown grubs are about 12 mm long. Grub period is 20 to 25 days.
Pupa: White and about 12 mm long. Pupation takes place in holes bored by the grubs. Pupal period is 5 to 7 days.
Adult: 10 to 16 mm long weevils, hard-shelled, with a rather long curved snout. Newly emerged weevils are red brown, turning almost black after a few days. They are free living, they are most commonly found between leaf sheaths, in the soil at the base of the mat or associated with crop residues. Weevils may live for up to two years, and can live without food for six months, but are very sensitive to desiccation and will die within 48 hours if kept in a dry substrate. They are active at night.
Cultural Control:
- Field sanitation
- Use clean planting material
- This can be done by selecting vigorous healthy planting material
- Trimming the suckers
- Hot water treatment of corms at 52 to 55°C for 15 to 27 minutes
- Suckers should be pruned periodically and infested pseudostems must be removed from the field and destroyed.
- Banana stumps kept in the field after harvest must be removed and destroyed as they serve as weevil refuges and breeding sites — Crop rotation with non host crops like paddy and sugarcane
- Use mechanical barriers in the field
- Ensure proper fertilization and free from weeds at all times
- Use mulch away from the banana stool leaving a clear ring about 60 cm from the base of the stool to keep the roots growing towards the surface and to avoid moist conditions near the stool, which will attract banana weevils
- Do not take regular crop in the same field to avoid initial infestation
- Removal of pseudo stems below ground level
- Avoid growing Robusta, Karpooruvally, Malbhog, Champa and Adukkar
- Grow less susceptible varieties like Poovan, Kadali, Kunnan, Poomkalli
Management-
- Field should be cleaned by removing the dried leaves and plant debris from the field and destroy it by burning or by dumping of leaves in mulching pit and covering with soil.
- Use healthy, uninfected sucker or rhizomes for planting time. Wash the suckers and dip in a solution of Chlorpyriphos 20 EC @ 2.5 ml/l before planting.
- Soil application of carbofuron@ 20g/plant during 3rd, 5th & 7th month after planting.
- Regular monitoring of weevil by keeping banana trap viz. (i) longitudinal cut stem trap of 30 cm size @ 10-15 per acre. In case once weevil is attracted to the laid traps, place longitudinal split banana traps @ 100 ha with bio control agents like entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana or entomopathogenic nematode, Heterorhabditis indica @ 20 g/trap.
Mechanical control:
- Pheromone lure (‘cosmolure’) can be used for monitoring as well as trapping of banana rhizome weevil. Installing traps at low trap density 2/acre.
- Initially placed in a line of 10 meters from a border and 20 meters apart.Chemical control:
- Soil incorporation at the time of planting carbofuran 3% CG @ 33g/sucker.
Chemical Control:
- Cut the banana plant after harvest at the ground level and treat it with carbaryl (1g/liter) or chlorpyriphos (2.5 ml/lit) at the cut surface.
- Application of Furadan 3G @ 20 gms or Phorate 10G @ 12 gms or Neem cake @ 1/2 Kg. per pit at planting.
- Before planting, the suckers should be dipped in 0.1 per cent quinalphos emulsion. Larva Pupa
- Dip the suckers in Monocrotophos solution (14 ml in 1 lit water) for about 20 minutes to kill the eggs and grubs of the corm weevil.
- Remove the pseudostem after harvest and treat it with Carboryl (1g/lit) or Chlorpyriphos (2.5ml/lit).
- Fumigation of banana plants using Celphos (aluminium phosphide tablets), especially during the vegetative phase is phytotoxic and should be discouraged.
- Apply castor cake 250g or carbaryl 50g dust or phorate 10g per pit before planting also prevents infestation. — Severe attack dimethoate, methyl demeton, or phosphamidon may be sprayed around the collar region.